Australian RCM Certification
date:2023-04-10 13:07:25
Certification Introduction
RCM certification is a logo introduced by Australia and New Zealand to achieve a unified logo for electrical products. The logo is a trademark owned by regulatory agencies in Australia and New Zealand, indicating that the product meets both safety and EMC requirements and is non-mandatory.
Australia RCM Information:
1. What is RCM registration?
RCM is the abbreviation of Regulatory Compliance Mark (Compliance Mark), which is the registration system for importers and manufacturers in Australia and New Zealand. From March 1, 2013, Australia began to enforce the new electronic and electrical equipment safety system (abbreviated as: EESS). RCM is the only conformity mark of the system, and only Australian importers or their authorized local agents can do it. Registered. The RCM mark covers electrical safety and EMC. SAA now provides EMC certification and SDoC (Supplier Declaration of Compliance). This service provides customers with the documents required by Australia.

2. What is the specified range of electrical equipment?
The specified range of electrical equipment is low-voltage electrical equipment within the following rated values:
• Greater than 50VAC RMS or 120VDC without ripple (extra low voltage);
• Less than 1000VAC RMS or 1500VDC without ripple (high voltage);
• Electrical equipment designed or sold for household, personal use or similar purposes.
3. There must be a responsible supplier for the electrical equipment within the specified range, but does it require RCM registration?
According to the current RCM system classification method, electrical equipment is divided into three categories, category 1 equipment, category 2 equipment and category 3 equipment, of which category 3 equipment is defined as high-risk equipment, and category 3 and category 2 equipment can be specified in relevant laws and regulations. AS/NZS 4417.2 query, this classification will change with the update of Australian standards/regulations. Now, RCM registration must be required for the 3 types of products. After the SAA Approvals agency issues the SAA certificate, the product certification information will be automatically imported into the RCM system to facilitate the RCM registration work for users.
4. The revised version of the RCM certification regulations AS/NZS 4417.2:2012 was officially enforced on January 14, 2017.
The relationship between SAA certification, C-Tick, A-Tick and RCM
SAA certification controls safety regulations, C-Tick certification controls EMC and radio products, and A-Tick certification controls telecommunications products. The RCM mark is a certification mark launched in 2013. After the product has obtained safety certification and electromagnetic compatibility registration, it can obtain the RCM mark through the safety certification regulatory agency. Starting from March 1, 2016, all electronic and electrical products sold must begin to use the RCM logo uniformly; the A-tick and C-tick logos will be replaced. RCM can be understood as a registration system, including SAA and C-TICK.

RCM certification (Australian Communications and Media Authority)
C-Tick, A-Tick and RCM are integrated into a single regulatory compliance mark RCM
Products must comply with electrical safety and electromagnetic compatibility
Agents need to log in to the national database
Need to apply for a certificate locally in Australia
RCM has fully replaced C-Tick and A-Tick on March 1, 2016
Australia RCM certification knowledge questions and answers
Q1. What are the REAS and RECS systems?
A1:REAS is the external certification system of New South Wales. They have a list of compulsory certification products. The products on the list are certified as Certificate of Approval. Such certificates are uploaded to the national database.
REAS overview:

RECS is Queensland's external certification system, which uses AS/NZS 4417.2 as the standard for products required by certification regulations. This means it covers all household products. The mandatory product list is very similar to the 3 product list. If you choose the RECS system, all certificates (categories 1, 2, 3) will be uploaded to the national database.
RECS overview:
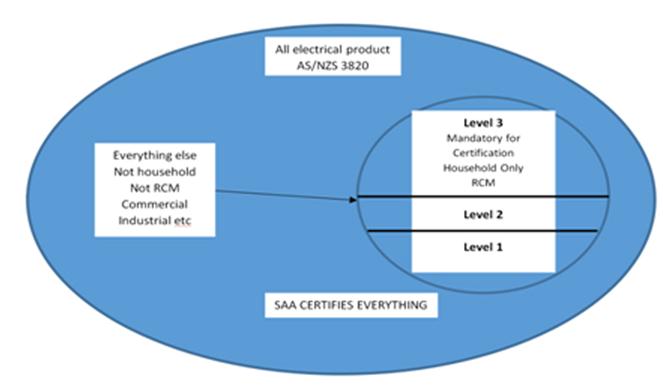
Q2. What is the specified range of electrical equipment?
A2: The electrical equipment in the specified range is the low-voltage electrical equipment within the following rated value range:
• Greater than 50VAC RMS or 120VDC without ripple (extra low voltage);
• Less than 1000VAC RMS or 1500VDC without ripple (high voltage);
• Electrical equipment designed or sold for household, personal use or similar purposes.
Q3. New RCM system
A3: RCM is just a sign, covering electrical safety and/or EMC.
No RCM certificate!!!
• Importers and manufacturers in Australia and New Zealand must register to use RCM.
• RCM is not applicable to the electrical safety of commercial products or industrial products.
• Even if a certain type of product is not covered by the electrical safety requirements of RCM, the product may still be required to be marked with RCM to prove compliance with EMC requirements.
• If you hold an SAA certificate and comply with EMC regulations, you can mark RCM on your products.
• Foreign companies cannot and need not register in the RCM system.
• When foreign manufacturers receive the SAA certificate, their compulsory certification products /3 products have been automatically registered in the RCM database. Importers can associate certificates in the system.
• If an electrical safety application uses the RECS system, we will still upload Type 1 and Type 2 certificates to the database.
• According to the current RCM system classification method, electrical equipment is divided into three categories, category 1 equipment, category 2 equipment and category 3 equipment, of which category 3 equipment is defined as high-risk equipment, and category 3 and category 2 equipment can be specified in relevant laws and regulations. AS/NZS 4417.2 query, this classification will change with the update of Australian standards/regulations. Now, RCM registration must be required for the 3 types of products. After the SAA Approvals agency issues the SAA certificate, the product certification information will be automatically imported into the RCM system to facilitate the RCM registration work for users.
Q4.EMC
A4: SAA now provides EMC certification and SDoC (Supplier Declaration of Compliance).
• This is not an agency service. This service provides customers with documents required by Australia.
• SAA issues legal documents required by Australian clients and government agencies.
Q5. Acceptable test report
A5: The report must be accompanied by a CNAS logo or similar logo.
• The report must be written according to the scope of laboratory accreditation.
• The signatory must be the signatory listed in the certification qualification document.
• If you submit a CB report, we also require a valid CB certificate. All CB reports mentioned in the certificate must be submitted. Please note: We do not accept CTF Stage 4 CB test reports.
• Starting from November 2018, GS reports are no longer accepted.
• All tests submitted to SAA must meet laboratory qualifications.
Q6. LED drive power
A6: Unless all connection points of the drive power supply use Z-type connections and are permanently fixed to the lamp, it is a compulsory product/3 product and requires separate certification.

Q7. LED portable lighting
A7: Compulsory certification products or category 3 products.
• AS/NZS 60598.1 and AS/NZS 60598.2.4.
• If the driving power supply is separated from the lighting lamp, the driving power supply must be certified separately.
• Appendix ZA is only suitable for simple lighting fixtures.

Q8. Power tools
A8: In Australia, portable hand-held power tools are compulsory certification products / category 3 products.
• Please note that many 60745 standards have been superseded by 62841.
• Mobile tool testing must comply with AS/NZS 62841, and IEC 61029 is no longer applicable.
• Must be tested according to published standards.
• Battery-powered electric tools must be tested according to AS/NZS 62841. As a complete component, the battery must comply with the IEC 62133 standard.
• Independent battery components sold separately are compulsory certification products in New Zealand and must be certified.
Q9. Power
A9: Must select the correct corresponding standard for testing according to the product;
• A/V, IT and communication devices can be tested according to AS/NZS 62368.1:2018;
• For 60950.1 or 60065, the time of discontinuation has not been determined, so these two standards can still be used for testing and applying for certification;
• ERAC issued a new announcement regarding the requirement for a plug-in power supply with two housing fixing methods. The requirements of this announcement only apply to direct plug-in power supplies that comply with the standards AS/NZS 61558 and AS/NZS 60335.2.29.
Q10. EPODs and controllers/regulators
A10: EPOD is a portable terminal block. Please note that it is portable.
• Applicable standards are AS/NZS 3105 or 3122 and 3100.
• The controller/regulator is a portable device. For fixed installations, other standards apply.
• AS/NZS 3105 is suitable for any EPOD with control/regulation function.

• The travel conversion socket must have only two sets of contacts and must meet the requirements of AS/NZS 3122.
• All references to AS/NZS 3100 series standards (such as 3105, 3112, 3133, 3122, etc.) and related tests required by AS/NZS 3100 must be completed and written in a test report.
• All switches must be bipolar disconnected and tested in the accessory products according to the M test clauses of AS/NZS 3133 or AS/NZS 60669.2.1 and 3133.
Q11. Solar inverter / DC isolating switch
A11: In Australia, such products must be registered with CEC.
• SAA certifies such products according to IEC 62109-1, IEC 62109-2 and AS/NZS 4777.2.
• If the product includes a battery at the same time, the battery must comply with the relevant IEC standards, and the inverter must also comply with AS 62040.1.1.
• The DC isolating switch used in the PV installation system now belongs to category 3 products and will soon be listed as a mandatory product. Must comply with AS/NZS 60947.3:2018, including all Australian standard deviations.
• AS/NZS 5033 is an installation standard and is not used for certification.
• AS/NZS 5039 is a planned battery energy storage installation standard. The standards committee is still in the process of making it and cannot be implemented in the short term. There is currently a new standard guidance document on battery energy storage preparation. CEC will soon be registered for battery energy storage preparation and DC disconnect switches used in PV preparation devices.

